ECC Newsletter August 2023
CEPT workshop unveils path to 6G advancements: a global endeavour towards extreme connectivity
A recent CEPT 6G workshop covered diverse topics, from aerospace and manufacturing to spectrum management and cybersecurity. It brought together industry experts and researchers to discuss the potential of 6G technology, writes Peter Faris and Jaime Afonso, ECO Spectrum Experts
The European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) workshop on 6G, which took place in Copenhagen on 29 and 30 June, unfolded an exciting vision for the future of mobile communications.
Organised by the ECO, the event brought together industry experts to discuss the evolution in mobile communication and the highly anticipated advancements of 6G. With its promise of extreme connectivity and immersive experiences, 6G has the potential to revolutionise the global mobile ecosystem.
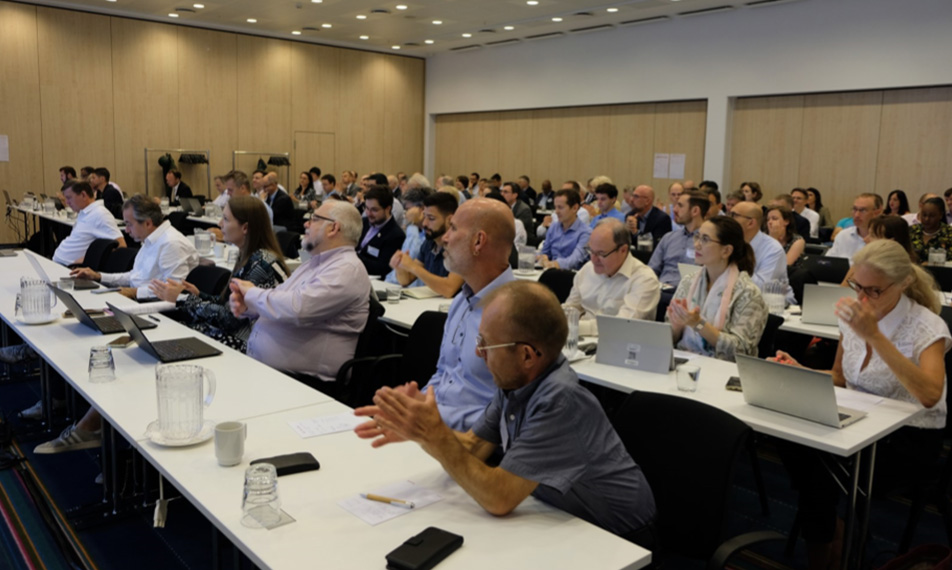

Figure 1: The workshop was attended by around 120 participants in Copenhagen and more following online
Harmonisation was a key theme emphasised during the workshop. If 6G is to be successfully introduced from around 2030 onwards, it will require global and regional alignment in terms of spectrum, standards and timing.
Availability of suitable spectrum is a critical factor for the success of next-generation wireless systems. At the event, speakers identified various spectrum ranges from lower/mid bands (up to 15 GHz) to sub-THz bands as possible candidates for 6G. They also identified different authorisation schemes, not just limited to traditional, licensed and licence-exempt models but also more novel approaches including local or light licensing. Identification of spectrum will need to consider the diverse needs of different applications. Holographic communications and immersive XR were noted as possible applications requiring additional spectrum.
Research and standardisation were also discussed at the workshop, featuring presentations from industry leaders such as Ericsson, Qualcomm and Nokia. These experts shed light on the roadmap towards 6G and the pivotal role of 5G Advanced in laying the foundation for 6G advancements.
Usage scenarios identified under this framework were introduced as essential elements for the seamless growth from 5G to 6G, including new elements of ubiquitous connectivity, integrated artificial intelligence (AI) and communication, as well as integrated sensing and communication.
Extensions to the familiar 5G "pillars" were also proposed where "immersive communication" would replace enhanced mobile broadband, "massive communication" would replace massive machine- type communication (mMTC), and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) would become "hyper" reliable (HRLLC).
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) release roadmap, as well as European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication (ITU-R) initiatives were discussed in this context. Particular attention was given to the recent completion of the draft ITU-R framework for 6G, known as "IMT-2030" in ITU terminology.
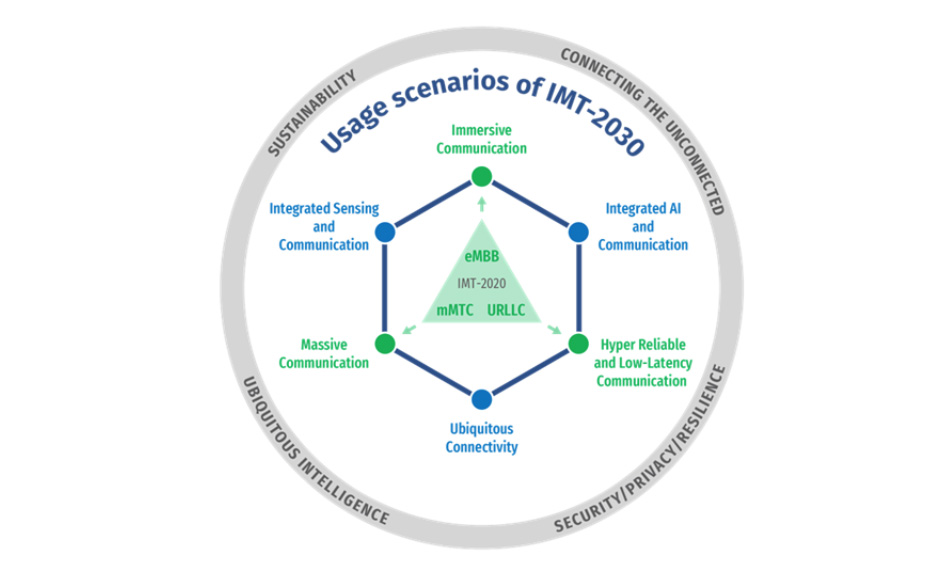
Figure 2: 6G usage scenarios from ITU-R framework for IMT-2030. Source: ITU-R internal document, 06/2023
The timeline for 6G specifications was outlined, with expectations that specifications will be available by 2028. 3GPP Release 19, planned for completion in 2025, is seen as a crucial milestone in enhancing 5G Advanced with cutting-edge capabilities, including energy efficiency, AI/machine learning, XR, sensing, and ambient Internet of Things. This progress will pave the way for the development and deployment of 6G technologies.
Advanced technological developments such as Giga MIMO, which combines the best of wide-band millimetre wave and wide area below 7 GHz, can play a role in facilitating these use cases.
AI is a hot topic at moment and its increasing role was noted by several speakers, both as an enabling technology for 6G as well as a use case, driving the need for additional bandwidth.
The role of non-terrestrial networks (NTN) to enable the goal of ubiquitous connectivity was explored by speakers in particular from Global Satellite Operators Association and the 6G-SKY project. The NTN vision is to develop a multi-layered "network of networks" which would encompass satellite constellations in various orbits as well as high altitude platform systems, aeroplanes and drones to complement coverage from ground-based networks.
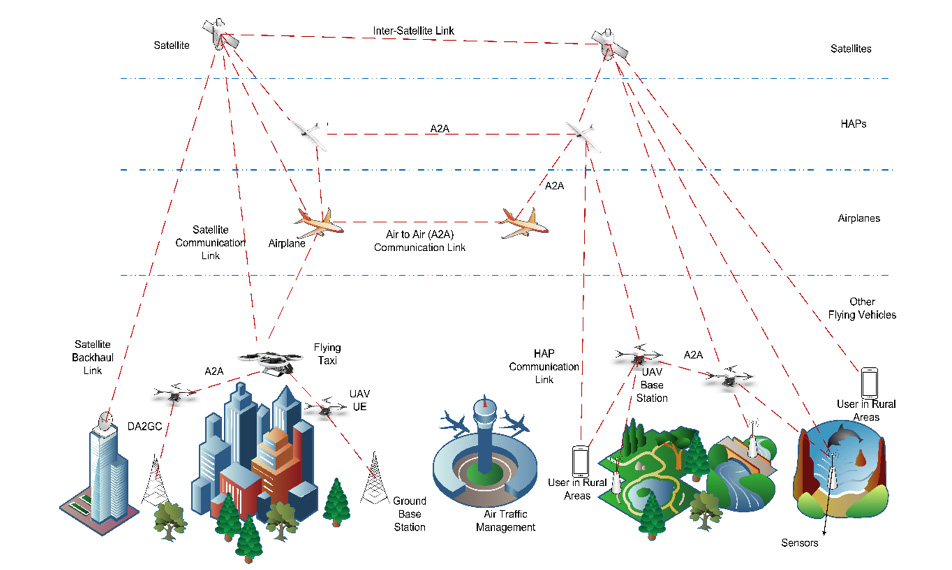
Figure 3: Overview of NTN connectivity scenarios. Source: 6G-SKY
Spectrum policy is a crucial aspect for the successful deployment of 6G. In this respect, the draft Radio Spectrum Policy Group opinion on 6G development was emphasised. This opinion considers among other things, the ongoing 5G implementation of primary and pioneer bands, the role and need for licence-exempt or light-licensed spectrum for offloading some of the 6G traffic, NTN to support 6G development, and to continue current initiatives on 5G.
During the workshop there was discussion on the respective spectrum needs of 6G and WiFi, with clear consensus that both will continue to grow and require access to spectrum. It was, however, less clear how the respective spectrum needs could best be met, how authorisation regimes may need to evolve, and how the networks themselves may be configured in future, not least to address indoor and outdoor demand. One speaker proposed that "indoor WiFi and outdoor 6G will bridge the digital divide together".
The progress of 5G deployment was also reviewed during the workshop. The European Telecommunications Network Operators' Association provided statistics on the population coverage of 5G in Europe compared to other regions and highlighted the importance of supportive policies for 5G deployment. Spectrum availability, harmonisation, and allocation were highlighted to ensure the success of 6G implementation.
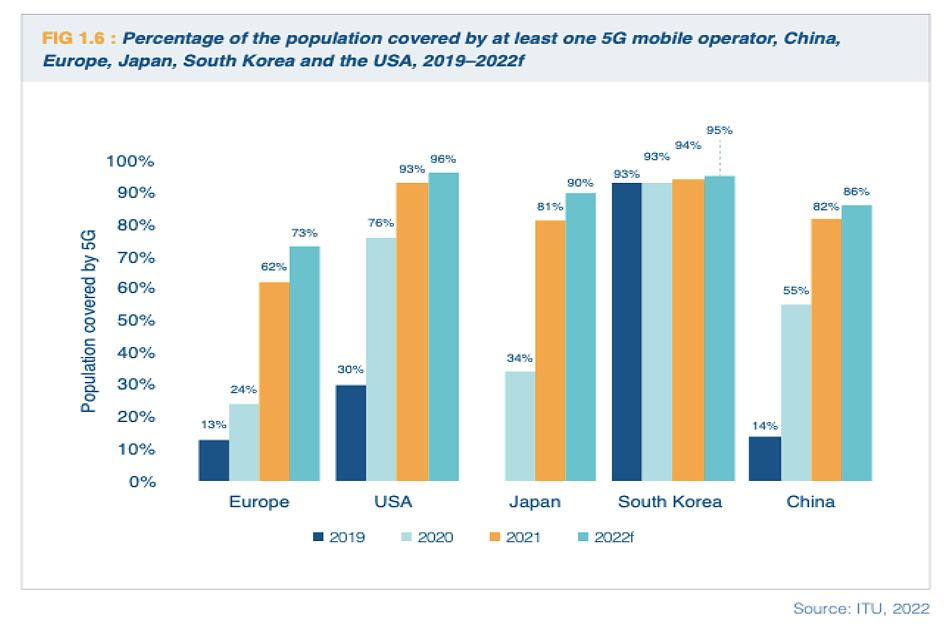
Figure 4: Percentage of population covered by 5G in Europe vs other regions. Source: ITU 2022, presented by ETNO
The suitability of different licensing approaches to meet the needs of 6G was also addressed in the workshop. The potential of spectrum sharing was noted, particularly in the context of new technologies. For example, antenna arrays can enable and improve sharing opportunities.
The needs for local and vertical users were presented, covering a diverse range of industries including aerospace, manufacturing and entertainment. Verticals and local licensing regimes have been discussed for some time and are now emerging as a reality, enabling innovation and new business models across a diverse range of sectors. The role of private networks was also discussed, for applications including autonomous quarrying vehicles and enterprise networks.
Beyond the spectrum domain, other topics including energy efficiency, cybersecurity and numbering were noted as important issues to be considered by CEPT administrations. On the latter, it was noted that it is extremely difficult to predict the demand for 6G number ranges and changes in assignment eligibility criteria. However, the use of numbers will continue to evolve and play a greater role behind the scenes in authentication, verification and call routing.
In conclusion, the workshop laid the groundwork for the anticipated 6G era, with global stakeholders collaborating to shape the future of extreme connectivity and immersive experiences. As research and development continue to progress, Europe and the world awaits the transformative potential that 6G may bring to the mobile landscape and beyond.
Presentations and photos from the workshop are available here.